The Undershoot Phase of After Hyperpolarization Is Due to
These inactivated sodium channels cannot open even if. B sustained opening of voltage-gated potassium channels.

Afterhyperpolarization Wikiwand
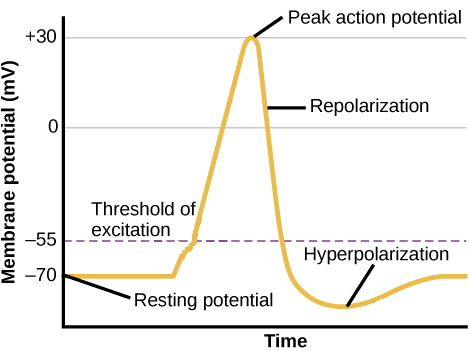
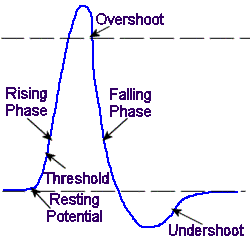
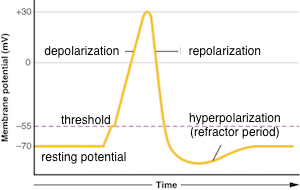
The falling phase is a rapid repolarization followed by the undershoot when the membrane potential hyperpolarizes past rest.

. More negative the normal resting potential of -70 mV ie up to -90 mV. This phase also known as undershoot phase. We studied the mecha-.
Answer outflow of the potassium ions Explanation - During after hyperpolarisation phase the resting membrane potential goes more negative. The positive currents flowing inward and outward become almost equal during this stage. D slow restorative actions of the sodium-potassium ATPase.
The rising phase is a rapid depolarization followed by the overshoot when the membrane potential becomes positive. Afterhyperpolarization or AHP describes the hyperpolarizing phase of a neurons action potential where the cells membrane potential falls below the normal resting potential. The Co inhibition can be.
In the resting cell K tends to leak out of the cell and Na leaks into the cell. However as tetanization proceeds a pattern of hyperpolarization develops with the result that in the tetanic steady state there exists a progressive hyperpolarization throughout each interspike interval. The undershoot was not present in traces without spikes.
The undershoot was probably caused by the activation of calcium-dependent Kand Clcurrents because these two ions had reversal potentials more negative than the rod membrane potential under our experimental conditions. During the afterhyperpolarization period after an action potential the membrane potential is more negative than when the cell is at the resting potential. A sodium ions entering the cell.
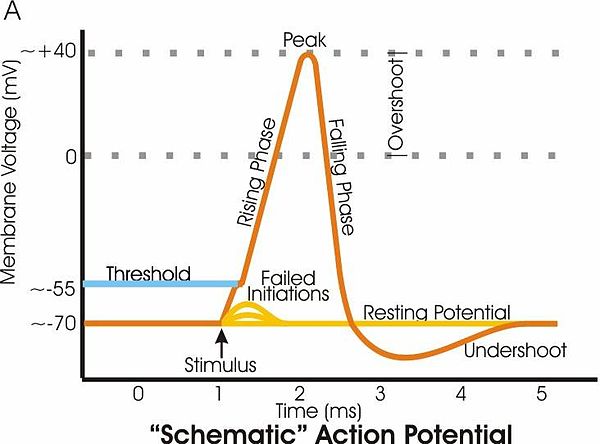
Neurons-Functional cells of the nervous system-Excitable cells-Communicate information in the form ofelectrical and chemical signals. The refractory period is primarily due to the inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels which occurs at the peak of the action potential and persists through most of the undershoot period. A slow opening of voltage-gated sodium channels.
During this phase opening of v. Finally the membrane potential will return to the resting membrane potential. The afterhyperpolarisation is one of the processes that contribute to the refactory period.
Due to rapid influx. The K conductance component increases in amplitude with increasing Ca concen- tration and is inhibited by extracellular Co. Images submitted without a detailed image list will not be considered.
This is also called the undershoot phase. This represents the initial part of the repolarization or phase 1. Redistribution of charge.
D slow restorative actions of the sodium-potassium ATPase. Artists may submit a maximum of 10 digital images. Overview of After Hyperpolarization.
Suggesting that it is due to an electrogenic Na pump. Other than this no other current flows due to hyperpolarization. The panel WILL NOT consider work samples that exceed the maximum.
The undershoot phase of after hyperpolarization is. Na through Na channels or Ca 2 through Ca 2 channels inhibits hyperpolarization. B sodium ions leaving the cell.
It is the opposite of a depolarization. Biol219 Lecture 11 Fall 2016 Dr Scott 2 The NaK pump maintains the K and Na gradients to maintain RMP over the long term. 21 The undershoot phase of after-hyperpolarization is due to.
Repolarization returns the membrane potential to the -70 mV value that indicates the resting potential but it actually overshoots that value. E ions that move away from their open ion channels. On the other hand influx of cations eg.
Across the axonal membrane. A large hyperpolarization that lasts seconds or minutes. 26 The undershoot phase of after-hyperpolarization is due to A slow opening of voltage-gated sodium channels.
30 _____The after-hyperpolarization undershoot phase of an action potential is due to excess. If a cell has Na or Ca 2. View the full answer.
Initially the interspike potential returns toward a resting level after this brief phase of hyperpolarization. Several recent investigations in the mammalian central nervous system have demon- strated thatanextracellular accumulation of Kresults from repetitive. C rapid opening of voltage-gated calcium channels.
Action potentialafter-hyperpolarizationundershootas anindex of extracellular Kconcentration andfoundthat withtrains ofimpulses K could build uptoabout twice the normal concentration. Get detailed expert explanations on after hyperpolarization that can improve your comprehension and help with homework. 29 The undershoot phase of after-hyperpolarization is due to _____.
CINTAS Foundation is offering a fellowship in the visual arts. After the end of the stimulation there is a transient K e-undershoot. Which occurs during the undershoot after an AP fires because K permeability becomes even greater than it is at rest.
Phase 2 is characterized by the plateau. Potassium ions reach equilibrium when the membrane voltage is below -70 mV so a period of hyperpolarization occurs while the K channels are open. To be eligible applicants must either have.
A slow opening of voltage-gated sodium channels B sustained opening of voltage-gated potassium channels C rapid opening of voltage-gated calcium channels D slow restorative actions of the sodium-potassium ATPase Answer. After the repolarizing phase of the action potential membrane permeability to potassium ions remains high which causes an undershoot or afterhyperpolarization phase until the membrane. Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K a cation through K channels or influx of Cl an anion through Cl channels.
Installation work may be accompanied by a video. The action potential undershoot is. This is also commonly referred to as an action potentials undershoot phase.
Learn all about after hyperpolarization. In the figure to the right this undershoot occurs at approximately 3 to 4 milliseconds ms on the time scale. B sustained opening of voltage-gated potassium channels.
Stimulus- and neurotransmitter-induced activity in the peripheral and central ner- vous system of mammals is accompanied by an elevation of the free extracellular K -concentration K k. C rapid opening of voltage-gated calcium channels.

Week 2 Membrane Potential And Nernst Equation Key Points For Resting Membrane Potential Ion Concentration Across The Membrane E Ion Equilibrium Potential Ppt Download
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy

Action Potentials Foundations Of Neuroscience

Solved 6 The Undershoot Phase Of After Hyperpolarization Chegg Com
Hyperpolarization Biology Wikiwand
Neuroscience A Journey Through The Brain The Action Potential


Comments
Post a Comment